Zero-Sum Game
Is life really winner takes all?
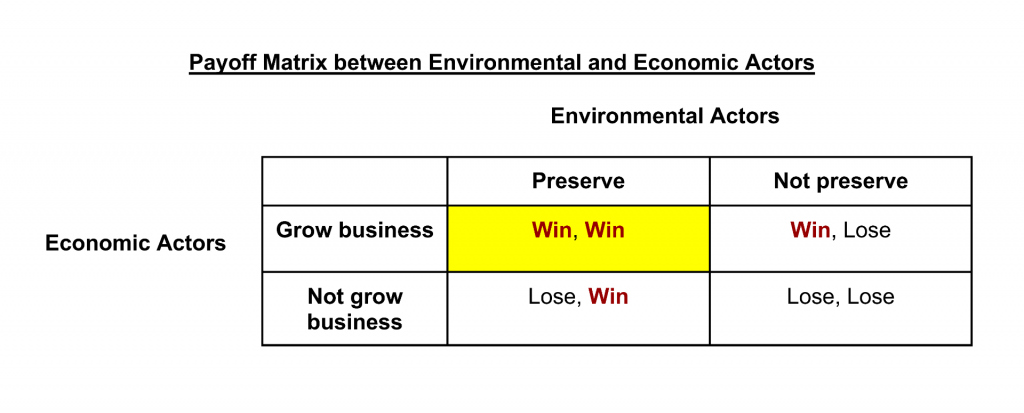
A zero-sum game is a concept from game theory, which is a branch of mathematics and economics that studies how people or entities make decisions in competitive situations. In a zero-sum game, the total gain (or loss) of one participant is exactly balanced by the total loss (or gain) of another participant or participants. This means that whatever one player wins, another player (or players) must lose an equal amount. In essence, the gains and losses among participants add up to zero.
This is most common in games where there are fixed resources that everyone is competing for. These resources are often finite. Think about how there is a maximum amount of money in a game of Monopoly. The Bank only has so much, and after a certain number of turns it becomes of game of passing money around based on which tiles you land on.
It's important to note that not all real-world situations are zero-sum games. Many situations allow for win-win outcomes, where participants can benefit without causing harm to others. In zero-sum games, the idea of a "win-win" is not possible because any gain by one participant must be balanced by an equal loss for another.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/zero-sumgame_final-f2202227bea2472ba9204f7ec61b962e.png)